 Testosterone
Testosterone for Dry Eye Syndrome
by Jeffrey Dach MD
Mrs. B was 58 years old with typical menopausal symptoms of night sweats and hot flashes, and came to see me because of dry itchy, red eyes. The lids sometimes swell because of the irritation. Over the years, Mrs B had been to numerous eye doctors who gave her various drops to lubricate the eye, antibiotic drops and steroid drops. She has been given instructions for cleaning and irrigating the eyes. The eye drops seem to help somewhat but the irritation always returns whenever she stops them. Lately, the condition is getting worse and nothing seems to help.
Above left image: courtesy of wikimedia commons, red arrow points to meibomian glands in edge of eye lid which secrete oil which lubricates the eye.
Low Testosterone Level
A routine hormone panel showed that Mrs B had low hormone levels, and her testosterone level was especially low. I explained to Mrs B that her dry eye syndrome was caused by low testosterone levels, and testosterone would help.
Cured With Testosterone, Surely You Must Be Joking, Doctor
Six week later, after starting her testosterone as sublingual drops, Mrs B reported her eyes were much better. She also started a complete bioidentical hormone program. Mrs B's ophthalmologist, Dr H, was an old friend of mine and we would occasionally attend the same social functions. At one of these social functions, Dr H approached to say that a patient (no name) reported that I had cured her dry eyes with testosterone, and surely you must be joking, Doctor. His gesture and facial expression with his eyes rolling back were quite distinctive.
Testosterone for Dry Eyes
in the Opthalmology Medical Literature
Apparently, Dr H is unaware of the supportive evidence in his own specialty medical journals. We will look at a few of these supportive articles that recommend testosterone for evaporative dry eye syndrome. About 5 million Americans have Dry Eye Syndrome caused by dysfunction of the lubricating glands, which are called the lacrimal and meibomian glands. The small glands at the upper outer eye are the lacrimal glands, and the meibomian glands are located in the eye lid at the upper and lower edges (see diagram below).
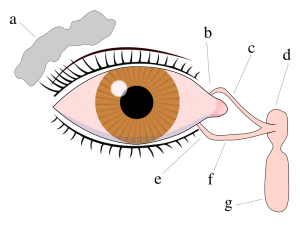 Left Image :Tear system: a. tear gland / lacrimal gland, b. superior lacrimal punctum, c. superior lacrimal canal, d. tear sac / lacrimal sac, e. inferior lacrimal punctum, f. inferior lacrimal canal, g. nasolacrimal canal.
Left Image :Tear system: a. tear gland / lacrimal gland, b. superior lacrimal punctum, c. superior lacrimal canal, d. tear sac / lacrimal sac, e. inferior lacrimal punctum, f. inferior lacrimal canal, g. nasolacrimal canal.Dr David A Sullivan and Dry Eye Research
Much of the research on testosterone and dry eyes has been done by David A Sullivan at Schepens Eye Research Institute at Harvard Medical School.(4)
Dr Sullivan Research in Mouse Model Of Sjogren's
Dr. Sullivan's early work in the 1990's involved Sjogrens syndrome, and the discovery that women with Sjögren's syndrome are androgen-deficient causing meibomian gland dysfunction, tear film instability, and the evaporative dry eye characteristic Sjogren's, which is an autoimmune disorder. (1) Sullivan published a study in 1991 which showed that testosterone inhibited the progression of autoimmune disease in the lacrimal glands mice with Sjogren's. His mouse model of Sjogren's showed that the testosterone suppressed the magnitude of lymphocyte infiltration in the lacrimal gland 22- to 46-fold.(6)
Lacrimal and Meibomian Glands Regulated by Testosterone
In a 1999 report, Sullivan suggested that androgens (testosterone) regulate both lacrimal and meibomian gland function, and suggest that eye drops containing testosterone may be safe and effective treatment for dry eyes in Sjögren's syndrome.(1)
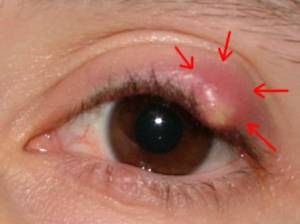 Left Image: Chalazion, obstructed, infected meibomian gland upper eye lid. This image is useful to give you an idea of where the glands are locared in the lid. There are 20 - 30 small Meibomian glands located along the edge of the upper and lower lid that secrete oil which lubricates the surface of the eye. When one becomes obstructed, it swells up and is called a Chalazion. Treatment is to relieve the obstruction and allow drainage. Courtesy of wikimedia commons.
Left Image: Chalazion, obstructed, infected meibomian gland upper eye lid. This image is useful to give you an idea of where the glands are locared in the lid. There are 20 - 30 small Meibomian glands located along the edge of the upper and lower lid that secrete oil which lubricates the surface of the eye. When one becomes obstructed, it swells up and is called a Chalazion. Treatment is to relieve the obstruction and allow drainage. Courtesy of wikimedia commons. Men on Testosterone Blockers Get Dry Eyes
In 2000, Dr Sullivan reported that men taking testosterone blockers have dry eye syndrome. Men on testosterone blocker drug treatment for prostate cancer were found to had poor quality of tear fluid. This was demonstrated by analyzing the meibomian gland secretions. Their dry eye symptoms included light sensitivity, painful and blurry eyes. Sullivan said,"the use of anti-androgen pharmaceuticals was associated with significant changes in the relative amounts of lipids in meibomian gland secretions. Our findings indicate that chronic androgen deficiency is associated with meibomian gland dysfunction and dry eye." (2)
In 2001, Drs Worda and Nepp from Vienna Austria reported that topically administered androgen can restore the lipid phase of the tear film, and was useful in treatment of keratoconjunctivitis sicca, medical terms for Dry Eyes. (3)
Complete Insensitivity to Androgen and Dry Eyes
Next, Dr Sullivan turned his attention to a genetic disorder called Complete Insensitivity to Androgen (CIAS). In this genetic disorder, the androgen receptor is nonfunctional, and subsequently, there is insensitivity to testosterone. Without a functioning receptor, the normal activity of testosterone is completely blocked.
Dr Sullivan examined the tears (ie. Meibomian gland secretions), in women with CIAS and compared them to normal controls. The patients with CIAS had alteration in the lipid fractions of tear fluid, ( ie meibomian gland secretions). This study was published in a 2002 report in Arch Ophthalmology (5).
Trans-Dermal Testostorone For Dry Eye Syndrome
In 2003, DrConnor reported transdermal testosterone is safe and effective treatment for dry eye, with the post-menopausal females having the greatest relief of symptoms. (10)
Molecular Biology Mouse Studies of Gene Expression
In 2005, Dr Schirra et al studied the molecular biology of testosterone, and gene expression in the meibomian gland of mice. Dr Schirra reported that testosterone regulates the expression of more than 1500 genes in the mouse meibomian gland which serves to stimulate lipid and fatty acid metabolism in the lubricating eye fluid.
(11)
The Evidence is Overwhelming
The sum total of the above evidence is overwhelming that testosterone playes a key role in production of oil, the lipid component for lubricating the eyes, and that testosterone deficiency is a treatable cause of dry eye syndrome. The treatment is testosterone, a bioidentical hormone.
_______________________________________________
For Articles with Related content: Testosterone Information Menu
Jeffrey Dach MD
7450 Griffin Rd Suite 180/190
Davie, FL 33314
Phone: 954-792-4663
Facebook
Blog
Links and References
(1) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10415627
Androgens and dry eye in Sjögren's syndrome.
Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Jun 22;876:312-24. Sullivan DA et al.
Our results demonstrate that androgens regulate both lacrimal and meibomian gland function, and suggest that topical androgen administration may serve as a safe and effective therapy for the treatment of dry eye in Sjögren's syndrome.
(2) http://jcem.endojournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/85/12/4874
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism Vol. 85, No. 12 4874-4882,2000
Effect of Androgen Deficiency on the Human Meibomian Gland and Ocular Surface
Kathleen L. Krenzer, M. Reza Dana, M. David Ullman, Jennifer M. Cermak, Dorothy B. Tolls, James E. Evans and David A. Sullivan
Schepens Eye Research Institute (K.L.K., M.R.D., J.M.C., D.A.S.), Brigham and Women’s Hospital (M.R.D., J.M.C.), Department of Ophthalmology, Harvard Medical School
The purpose of this study was to determine whether the chronic use of antiandrogen medications leads to meibomian gland dysfunction, altered lipid profiles in meibomian gland secretions, decreased tear film stability, and evaporative dry eye.
Subjects taking antiandrogen therapy for prostatic indications, as well as age-related controls, were asked to complete a questionnaire that assessed dry eye symptoms and then were given a complete anterior segment examination. Moreover, meibomian gland secretions were obtained from each eye and analyzed by high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry for the relative content of cholesterol, cholesterol esters, wax esters, diglycerides, triglycerides, and specific molecular species in the diglyceride fraction.
Our results demonstrate that patients taking antiandrogen treatment, compared with age-related controls, had a:
1) significant increase in the frequency of appearance of tear film debris, an abnormal tear film meniscus, irregular posterior lid margins, conjunctival tarsal injection, and orifice metaplasia of the meibomian glands;
2) significant increase in the degree of ocular surface vital dye staining;
3) significant decrease in the tear film breakup time and quality of meibomian gland secretions; and
4) significant increase in the frequency of light sensitivity, painful eyes, and blurred vision.
In addition, the use of antiandrogen pharmaceuticals was associated with significant changes in the relative amounts of lipids in meibomian gland secretions. Our findings indicate that chronic androgen deficiency is associated with meibomian gland dysfunction and dry eye.
(3) http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11173183
Maturitas. 2001 Jan 31;37(3):209-12.
Treatment of keratoconjunctivitis sicca with topical androgen.
by Worda C, Nepp J, Huber JC, Sator MO. Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Division of Gynecological Endocrinology and Reproductive Medicine, Vienna University Hospital, Währinger Gürtel 18-20, 1090, Vienna, Austria.
OBJECTIVE: Androgens have been reported to influence lipid production of sebaceous glands and even many ocular tissues. The effect of topical androgen therapy on a 54-year-old patient with keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS) and decreased lipid phase of the tear film is reported.
METHODS: For assessment of the lipid phase of the tear film, break up time (BUT) and lipid layer thickness (LLT) were monitored during 6 months before treatment as well as 3 months while using a daily topical androgen therapy.
RESULTS: During the topical androgen therapy the pathological lipid phase of the tear film was completely restored indicated by the normalisation of the values of BUT and LLT.
CONCLUSION: These findings are consistent with animal experiments indicating that topical administered androgen can restore the decreased lipid phase of the tear film. This may open up new therapeutic strategies for KCS.
(4) http://www.schepens.harvard.edu/profiledevid/david-sullivan-phd/profile.html
Sullivan research summary at Schepens Harvard Medical School
we have shown that dry eye syndromes occur predominantly in women and that estrogen replacement therapy increases the prevalence of dry eye signs and symptoms in postmenopausal women. This latter finding is extraordinary, given that many millions of women worldwide are prescribed estrogen to alleviate menopausal symptoms and are therefore at heightened risk of developing dry eye. The precise mechanism(s) underlying the sex-related difference in, and the estrogen effect on, dry eye prevalence is unclear. However, we hypothesize that: [a] androgen deficiency and estrogen use are key factors in the predominance of dry eye syndromes in women; and [b] sex, androgen and estrogen effects are mediated through the regulation of gene expression in the cornea and the lacrimal and meibomian glands.
(5) http://www.aissg.org/PDFs/BD-Sullivan-CAIS-Meibomian-2002.pdf
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12470144
Arch Ophthalmol. 2002 Dec;120(12):1689-99.
Complete androgen insensitivity syndrome: effect on human meibomian gland secretions. by Sullivan BD, Evans JE, Cermak JM, Krenzer KL, Dana MR, Sullivan DA. Schepens Eye Research Institute,
OBJECTIVE: To determine whether androgen receptors affect the fatty acid profiles of neutral and polar lipids in human meibomian gland secretions.
METHODS: Meibomian gland secretion samples were obtained from both eyes of
(1) women with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome, a condition characterized by dysfunctional androgen receptors, and (2) age-matched female and male controls.
Samples were processed for high-performance liquid chromatography, mass spectrometry, or both and for analysis of the mass spectra of neutral and polar lipid fatty acid fragment ions by 3 different methods.
RESULTS: Androgen receptor dysfunction is associated with significant alterations in the appearance of numerous molecular species in the neutral and polar lipid fractions of meibomian gland secretions. The ability to detect these differences, and to assess their nature and extent, was facilitated by the use of several analytic approaches. Sex-related differences exist in the expression of a variety of neutral and, especially, polar fatty acid products in meibomian gland secretions.
CONCLUSIONS: Androgens exert a significant effect on neutral and polar lipids in human meibomian gland secretions, and these hormonal effects may be mediated through androgen receptors.
Sjogren's syndrome
(6) http://www.iovs.org/cgi/reprint/32/11/3002.pdf
http://www.iovs.org/cgi/content/abstract/32/11/3002
Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, Vol 32, 3002-3006.1991
Testosterone-induced suppression of autoimmune disease in lacrimal tissue of a mouse model (NZB/NZW F1) of Sjogren's syndrome AC Vendramini, C Soo and DA Sullivan Department of Ophthalmology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA 02114.
The current investigation was designed to examine whether androgen administration might suppress autoimmune disease in lacrimal glands of a mouse model (NZB/NZW F1) of Sjogren's syndrome. Autoimmune, female mice were treated with vehicle or varying concentrations of testosterone for 0, 17, 34, or 51 days, and tears, lacrimal glands, as well as submandibular tissue, were collected from killed mice after androgen exposure. Glands were histologically processed and evaluated with a computer-assisted image analysis system.
Results showed that testosterone administration induced a significant, time-dependent decrease in the extent of lymphocytic accumulation in the lacrimal gland. After 34-51 days of androgen therapy, the magnitude of lymphocyte infiltration had been suppressed 22- to 46-fold, compared with that in placebo-treated tissue. This hormone effect was associated with significant reductions in the number of focal infiltrates, the area of individual foci, and the total quantity of lymphocyte infiltration per lacrimal section. Testosterone exposure also stimulated an increase in lacrimal gland weight and a rise in tear volumes, relative to those measured in the same mice before treatment. In addition, androgens significantly diminished the extent of lymphocyte accumulation in submandibular tissue.
In summary, our results demonstrate that androgen administration may inhibit the progression of autoimmune disease in lacrimal and submandibular glands of NZB/NZW F1 mice.
(7) http://www3.interscience.wiley.com/journal/120778210/abstract
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12114274
Sullivan DA et al. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2002 Jun;966:211-22.
Androgen Deficiency, Meibomian Gland Dysfunction, and Evaporative Dry Eye
Abstract: Objective. We have recently discovered that women with primary and secondary Sjögren's syndrome are androgen-deficient. We hypothesize that this hormone insufficiency contributes to the meibomian gland dysfunction, tear film instability, and evaporative dry eye that are characteristic of this autoimmune disorder. If our hypothesis is correct, we predict: (1) that androgens regulate meibomian gland function, control the quality and/or quantity of lipids produced by this tissue, and promote the formation of the tear film's lipid layer; and (2) that androgen deficiency, due to an attenuation in androgen synthesis (e.g., during Sjögren's syndrome, menopause, aging, complete androgen-insensitivity syndrome [CAIS] and anti-androgen use), will lead to meibomian gland dysfunction and evaporative dry eye.
Methods. Experimental procedures included clinical studies, animal models, and histological, biochemical, molecular biological, and biomedical engineering techniques.
Results. (1) androgens regulate the meibomian gland. This tissue contains androgen receptor mRNA, androgen receptor protein within acinar epithelial cell nuclei, and Types 1 and 2 5a-reductase mRNAs. Moreover, androgens appear to modulate lipid production and gene expression in mouse and/or rabbit meibomian glands; and
(2) androgen deficiency may lead to meibomian gland dysfunction, altered lipid profiles in meibomian gland secretions, tear film instability, and evaporative dry eye. Thus, we have found that anti-androgen therapy in men is associated with meibomian gland disease, a decreased tear film breakup time, and functional dry eye.
Furthermore, we have discovered that androgen receptor dysfunction in women with CAIS is associated with meibomian gland changes and a significant increase in the signs and symptoms of dry eye. Of interest, we have also found that androgen deficiency is associated with significant and striking alterations in the neutral and polar lipid patterns of human meibomian gland secretions.
Conclusions. Our findings show that the meibomian gland is an androgen target organ and that androgen deficiency may promote meibomian gland dysfunction and evaporative dry eye. Overall, these results support our hypothesis that androgen deficiency may be an important etiologic factor in the pathogenesis of evaporative dry eye in women with Sjögren's syndrome.
(8) http://www.aissg.org/INDEX.HTM
Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome or AIS
(old name Testicular Feminization Syndrome or Testicular Feminisation Syndrome).
(9)http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Androgen_insensitivity_syndrome
The incidence of complete AIS is about in 1 in 20,000. Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome is a phenotypic female with a chromosomal genotype of 46,XY.The Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome has been linked to mutations in AR, the gene for the human Androgen Receptor, located at Xq11-12 (i.e. on the X chromosome).
The principal androgens are testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).The androgen receptor (AR) is a large protein of at least 910 amino acids. Each molecule consists of a portion which binds the androgen, a zinc finger portion that binds to DNA in steroid sensitive areas of nuclear chromatin, and an area that controls transcription.
(10) http://abstracts.iovs.org/cgi/content/abstract/44/5/2450
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2003;44: E-Abstract 2450.
Treatment of Dry Eye with a Transdermal 3% Testosterone Cream
by C.G. Connor Optometry, Southern College of Optometry, Memphis, TN, United States
Sullivan and colleagues have shown androgens play a key role in regulating the function of both the lacrimal and meibomian glands. Previous work from our laboratory has shown that androgenic supplemented artificial tears were effective in relieving the symptoms of dry eye. The poor solubility of androgens resulted in considerable irritation and poor patient compliance. The present study employs transdermal delivery of testosterone to treat dry eye.
Methods:Twenty eight subjects 3 males and 25 females with a mean age of 52.5 yrs that ranged from 25 to 76 yrs. with a subjective complaint of dry eye were enrolled in the study. The subjects were divided into two groups.
One group received the transdermal cream alone, while the second group used the transdermal cream supplemented with 3% testosterone. The subjects applied the cream 2 times daily for two weeks. The groups were reversed after two weeks of cream use. Baseline TBUT(tear breakup time) and Schirmer test were done prior to the study and after the use of each the two transdermal creams(control and testosterone).
Results:Baseline TBUT was 3.83 +/- 2.07 sec, testosterone was 4.13 +/- 1.83 sec, and cream alone was 4.53 +/- 2.2 sec. Schirmer results are 8.53 mm+/- 5.27 in 5 min baseline , 11.5 mm +/- 5.8 testosterone, and 7.8mm +/- 4.4 cream alone. ANOVA with post hoc student Newman-Keuls reveals that the Schirmer test results with 3% testosterone is different from baseline and cream alone at p=.05 level.
Over half the subjects reported significant improvement in dry eye symptoms with the testosterone cream.
Conclusion:Transdermal delivery of testosterone appears to be a safe and effective treatment for dry eye. The transdermal cream allows use of increased testosterone concentration and dramatically improves patient comfort. Post-menopausal females perceived the greatest relief of symptoms from the treatment, while males had the least benefit.
(11) http://www.iovs.org/cgi/content/full/46/10/3666
Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science. 2005;46:3666-3675.)
Androgen Control of Gene Expression in the Mouse Meibomian Gland by Frank Schirra,1,2 Tomo Suzuki,1,2 Stephen M. Richards,1 Roderick V. Jensen,3 Meng Liu,1,2 Michael J. Lombardi,3 Patricia Rowley,3 Nathaniel S. Treister,1,4 and David A. Sullivan1,2
From the Schepens Eye Research Institute, and the 2Department of Ophthalmology, Harvard Medical School, Boston, Massachusetts
PURPOSE. In prior work, it has been found that the meibomian gland is an androgen target organ, that androgens modulate lipid production within this tissue, and that androgen deficiency is associated with glandular dysfunction and evaporative dry eye. This study’s purpose was to test the hypothesis that the androgen control of the meibomian gland involves the regulation of gene expression.
METHODS. Meibomian glands were obtained from orchiectomized mice that were treated with placebo or testosterone for 14 days. Tissues were processed for the analysis of differentially expressed mRNAs by using gene bioarrays, gene chips, and real-time PCR procedures. Bioarray data were analyzed with GeneSifter software (VizX Labs LLC, Seattle, WA).
RESULTS. The results show that testosterone influenced the expression of more than 1590 genes in the mouse meibomian gland. This hormone action involved a significant upregulation of 1080 genes (e.g., neuromedin , and a significant downregulation of 518 genes (e.g., small proline-rich protein 2A). Some of the most significant androgen effects were directed toward stimulation of genes associated with lipid metabolism, sterol biosynthesis, fatty acid metabolism, protein transport, oxidoreductase activity, and peroxisomes.
CONCLUSIONS. These findings demonstrate that testosterone regulates the expression of numerous genes in the mouse meibomian gland and that many of these genes are involved in lipid metabolic pathways.
http://archopht.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/full/122/2/151
Dry Eye Signs and Symptoms in Women With Premature Ovarian Failure
Janine A. Smith, MD; Susan Vitale, PhD, MHS; George F. Reed, PhD; Shirley A. Grieshaber, RN, CRNO; Linda A. Goodman, COT; Vien H. Vanderhoof, RN, CRNP; Karim A. Calis, PharmD, MPH; Lawrence M. Nelson, MBA, MD Arch Ophthalmol. 2004;122:151-156.
Objective To examine whether women with premature ovarian failure (POF) have abnormal findings in ocular surface or tear parameters and whether they report symptoms of ocular discomfort compared with age-matched controls.
Methods Sixty-five patients with POF and 36 age-matched healthy controls were examined for signs and symptoms of dry eye. The Ocular Surface Disease Index questionnaire and the 25-item National Eye Institute Visual Function Questionnaire (NEI-VFQ 25) were administered to the participants. Assessments of ocular surface damage (Oxford and van Bijsterveld scores of vital dye staining) and tear status (Schirmer tests 1 [without anesthesia] and 2 [with anesthesia] and tear breakup time) were performed.
Results Women with POF scored significantly worse than controls on all ocular surface damage parameters: Oxford score (3.2 vs 1.7; P = .001), conjunctival lissamine green (2.1 vs 1.3; P = .02), corneal fluorescein staining (1.2 vs 0.4; P = .005), and van Bijsterveld score (2.1 vs 1.3; P = .02). Further, the proportion of patients with POF meeting the dry eye diagnostic criterion of a van Bijsterveld score greater than or equal to 4 was significantly greater among women with POF than among controls (20% vs 3%; P = .02). The POF group also tended to have worse scores than controls on self-reported symptoms, as measured by the overall Ocular Surface Disease Index (12.5 vs 2.1; P<.001) and the overall NEI-VFQ (94 vs 98; P = .001) after adjustment for age and race. Schirmer test scores and tear breakup time did not differ.
Conclusions Women with POF were more likely to exhibit ocular surface damage and symptoms of dry eye than age-matched controls. They were not, however, more likely to have reduced tear production. To our knowledge, this association between ocular surface disease and POF has not been previously reported. These data provide further evidence of the multifaceted role of sex hormones in the health and disease of the ocular surface.
http://www.tearfilm.org/dewsreport/pdfs/TOS-0502-DEWS-noAds.pdf
Based on data from the largest studies of dry eye to date, the Women’s Health Study (WHS), and the Physicians’ Health Study (PHS), and other studies,3-14 it has been estimated that about 3.23 million women and 1.68 million men, for a total of 4.91 million Americans 50 years and older have dry eye.
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Tear_system.svg
lacrimal gland Tear system:
a. tear gland / lacrimal gland,
b. superior lacrimal punctum,
c. superior lacrimal canal,
d. tear sac / lacrimal sac,
e. inferior lacrimal punctum,
f. inferior lacrimal canal,
g. nasolacrimal canal
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meibomian_gland
The Meibomian glands are the 25-30 oil-producing glands located in both the upper and lower eyelids that release oil slowly into the tear film. This oil helps to stop the water in the tears from evaporating, so helping to prevent dry eyes.
Dysfunctional meibomian glands often cause dry eyes, one of the more common eye conditions. They may also cause blepharitis, as the dry eyeball rubs off small pieces of skin from the eyelid, which may get infected. Inflammation of the meibomian glands (also known as meibomitis, meibomian gland dysfunction, or posterior blepharitis [1]) causes the glands to be obstructed by thick secretions, the resulting swelling is termed a chalazion. Besides leading to dry eyes, the obstructions can be degraded by bacterial lipases, resulting in the formation of free fatty acids, which irritate the eyes and sometimes cause punctate keratitis.
Jeffrey Dach MD
7450 Griffin Road Suite 190
Davie, Florida 33314
954-792-4663
http://www.jeffreydachmd.com
http://www.drdach.com/
http://www.naturalmedicine101.com/
http://www.truemedmd.com/
http://www.bioidenticalhormones101.com/
For Disclaimer: Click Here
The reader is advised to discuss the comments on these pages with
his/her personal physicians and to only act upon the advice of his/her
personal physician. Also note that concerning an answer which appears as
an electronically posted question, I am NOT creating a physician —
patient relationship.
Although identities will remain confidential as much as possible, as I can not control the media, I can not take responsibility for any breaches of confidentiality that may occur.
Copyright (c) 2014 Jeffrey Dach MD All Rights Reserved
This article may be reproduced on the internet without permission,
provided there is a link to this page and proper credit is given.
FAIR USE NOTICE: This site contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of issues of significance. We believe this constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes.
Serving Areas of: Hollywood, Aventura, Miami, Fort Lauderdale, Pembroke Pines, Miramar, Davie, Coral Springs, Cooper City, Sunshine Ranches, Hallandale, Surfside, Miami Beach, Sunny Isles, Normandy Isles, Coral Gables, Hialeah, Golden Beach ,Kendall,sunrise, coral springs, parkland,pompano, boca raton, palm beach, weston, dania beach, tamarac, oakland park, boynton beach, delray,lake worth,wellington,plantation