 Screening Mammograms,
Screening Mammograms, A Closer Look at the Data
by Jeffrey Dach MD
A 2009 article by Dr. Laura Esserman published in JAMA questions screening mammography.
Dr Esserman reviewed 20 years of data and concludes mammogram screening programs have "significant drawbacks and expected survival benefits have not materialized. While the incidence of early stage breast cancer has decreased due to mammography, the incidence rates for the killer cancers, (the advanced cancers) have remained stable. While it is true that overall mortality rates have declined slightly, this is attributed to better treatment rather than increased detection." quoted from (1)
Let's take a look at the data charts Dr Esserman used for her article in Jama 2009 (1). (see below)
Below Image Courtesy of JAMA. 2009;302(15):1685-1692.(1)
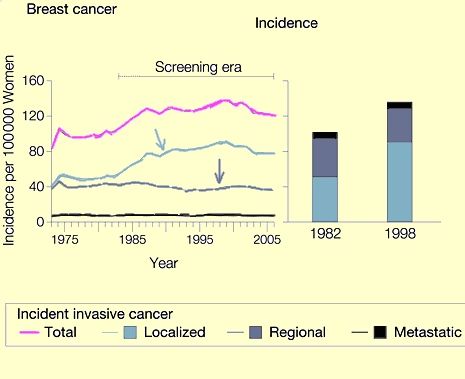
The above chart shows the critical information in Dr Esserman's JAMA article. The Pink line is TOTAL breast cancer incidence annually. Note increase incidence beginning in 1983 with introduction of mammography screening. Below the pink line, we see three more lines: this is the breakdown of the total incidence into localized, regional and metastatic cases. The turquoise line is localized cancer. The Light purple line is regional cancer and the black line (lowest) is metastatic cancer. The killer cancers are the regional and metastatic cases. Note that these numbers have remained stable with little change in spite of detection of massive numbers of localized cases
Here is another chart looking at incidence and mortality from breast cancer annually (below) (all cases):

Source for above two charts: http://caonline.amcancersoc.org/cgi/content/full/59/4/225
Figure 3 and Figure 4 combined, FIGURE 3 (upper pink line) Annual Age-adjusted Cancer Incidence Rates among Females for Breast Cancer, United States, 1975– 2005. FIGURE 4 (lower pink line) Annual Age-adjusted Cancer Death Rates among Females for Breast Cancers, United States, 1930–2005.
The upper pink line (red arrow) is the incidence of breast cancer since 1976. Notice the dramatic increased detection of cases in the early 1980's with introduction of screening mamography. The lower pink line (green arrow) is the annual mortality rate for breast cancer from 1930 to 2006. Note this is stable at about 30 cases per 100,000 women, and declines over the last section (green arrow) to about 25 cases per 100,000. Dr Esserman suggests this rather modest decline in mortality (green arrow) is not due to increased detection with mammography, rather it is due to improvement in treatment.
Annual Breast Cancer Mortality - Where's the Benefit?
While the incidence of early stage breast cancer has decreased by 2.8% per year since 2001, incidence rates of advanced (distant-stage) disease have remained stable.(link). In 2009, 192,370 women will be diagnosed with breast cancer and 40,170 women will die of breast cancer.(link) Mammography has increased the detection of very early stage cancer, called DCIS, with 60,000 cases of DCIS detected annually.
Esserman's 2009 Observations were made in 2002 by Barnett Kramer
 Seven years ago, Dr. Barnett Kramer, director of the Office of Disease Prevention at the National Institutes of Health, was interviewed in a 2002 article in the New York Times, in which said: "The number of women with breast cancers with the worst prognosis, those that spread to other organs, had been fairly constant in the years before mammography was introduced, and that trend did not change after the introduction of mammography...If screening worked perfectly, every cancer found early would correspond to one fewer cancer found later. That did not happen. Mammography, instead has resulted in a huge new population of women with early stage cancer but without a corresponding decline in the numbers of women with advanced cancer."
Seven years ago, Dr. Barnett Kramer, director of the Office of Disease Prevention at the National Institutes of Health, was interviewed in a 2002 article in the New York Times, in which said: "The number of women with breast cancers with the worst prognosis, those that spread to other organs, had been fairly constant in the years before mammography was introduced, and that trend did not change after the introduction of mammography...If screening worked perfectly, every cancer found early would correspond to one fewer cancer found later. That did not happen. Mammography, instead has resulted in a huge new population of women with early stage cancer but without a corresponding decline in the numbers of women with advanced cancer."Weighing the Pluses and Minuses of Screening Mammography
Dr Gilbert Welch in his BMJ editorial, says the following about mammography screening for breast cancer:
•1 in 1,000 women annually screened for 10 years will avoid dying from breast cancer.
•2 to 10 women will be over-diagnosed and treated needlessly
•10 to 15 women will be told they have breast cancer earlier than they would otherwise have been told, but this will not affect their prognosis.
•100 to 500 women will have at least one "false alarm" (about half of these women will undergo a biopsy)
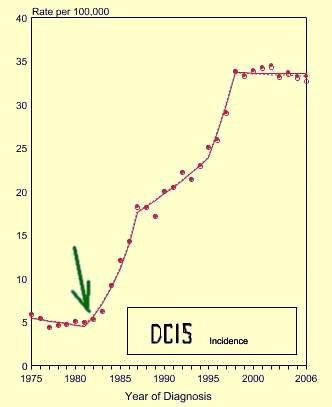 Mammography Finds the DCIS Lesions
Mammography Finds the DCIS Lesions Left chart shows annual incidence of DCIS (ductal carcinoma in situ). Note huge increase in 1983 (green arrow) with introduction of screening mammography.
Finding the Reservoir of DCIS
Mammography screening finds the small indolent cancers called DCIS that represent a reservoir of silent disease in up to 18% of the population (at autopsy). This leads to overdiagnosis and overtreatment. For the invasive cancers found in 1-2% of the population (at autopsy series), screening detection is of little help, with little change in the number of advanced cancer cases, and about 40,000 deaths every year.
Source above left image: SEER Cancer Statistics Review 1975-2006
Dr. Gilbert Welch sums it up with the following sage advice: "doctors who recommend less-aggressive mammography (less frequently, waiting until you are age 50, or stopping it when you are older) or are less quick to biopsy may not be bad doctors but good ones."
 Just Stop Calling It Cancer - DCIS
Just Stop Calling It Cancer - DCIS
One glaring problem with screening mammography is the detection of DCIS at a rate of 60,000 case per year. DCIS is ductal carcinoma in situ, a pathology diagnosis which carries a very good prognosis, a 98% - 5 year survival with no treatment. In spite of the rather benign natural history of DCIS, mainstream medicine treats these lesions aggressively with surgery and radiation. Recently, the NIH has called for a change in terminology, asking pathologists to stop calling it "cancer".
Left Image : typical appearance of DCIS with punctate calcifications on mammogram (arrow). Courtesy Wikimedia Commons.
Here is the NIH consensus statement: "Because of the noninvasive nature of DCIS, coupled with its favorable prognosis, strong consideration should be given to elimination of the use of the anxiety-producing term “carcinoma” from the description of DCIS. "
Just Stop Calling it Thyroid Cancer
A similar proposal has been made for papillary thyroid cancer, requesting a change in terminology, and just stop calling it "cancer". In the 2003 issue of the International Journal of Surgical Pathology, Dr Rosai presented the Porto Proposal , in which he suggested using the terminology, papillary microtumor instead of thyroid cancer.
Just Turn Off the Ultrasound Machines !
An exasperated radiologist, John J. Cronan, MD says in the June 2008 issue of Radiology we should "turn off the ultrasound machines". Cronan questions this entire medical enterprise of detecting thyroid nodules, and small cancers with ultrasound guided biopsy. The thyroid has a large reservoir of clinically insignificant disease, and we are now realizing that screening thyroid nodules for cancer with ultrasound does more harm than good.
A Large Reservoir of Silent Disease - For All Three
All three types of cancer, breast, thyroid and prostate have a large reservoir of indolent or biologically insignificant disease that remains silent during the patient's lifetime. We know this from autopsy studies. One autopsy study of 110 women from Finland using specimen radiographs of thin sections found breast cancer in 20% of the cases. (2 % had invasive cancer, and 18% of the 110 cases had In-Situ Cancer).
 Spontaneous Remission of Breast Cancer ?
Spontaneous Remission of Breast Cancer ?
One screening study reported by Welch in the Annals of Internal Medicine actually concluded that many small breast cancers spontaneously regress. Gina Kolata wrote a New York Times piece about it. Actually, spontaneous regression of breast cancer has been reported. Sir William Osler, a legendary and revered doctor reported 14 cases himself.
See this 1901 report: The Medical Aspects of Carcinoma of the Breast, with a Note on the Spontaneous Disappearance of Secondary Growths, OSLER W., American Medicine: April 6 1901; 17-19; 63-66. Perhaps breast cancer remission was more common during his lifetime.
Left Image: Breast Cancer Awareness Month with Pink Ribbons. Courtesy of WIkimedia Commons.
The real challenge is for medical science to investigate spontanous regression, and once understood, use it induce a cure in the cancer patient, thereby winning the war against cancer. Perhaps a mouse model discovered in 2003 showing spontaneous regression of advanced cancer in genetically determined mice could help make some progess with this research. This would be a good subject for an NIH grant.
Diagnosis is Not Screening
We must be careful about the difference between screening, and diagnosis. Screening pertains to mass screening of a healthy population. We had found this leads to overdiagnosis and overtreatment. Diagnosis pertains to evaluation and workup of a symptomatic patient, which is what the doctor does every day. PSA testing, mammography and ultrasound remain excellent diagnostic tools for workup and evaluation of the symptomatic patient.
How to Prevent Breast Cancer
1) Vitamin D Supplementation.
2) Iodine Supplementation (see left image: Iodoral)
3) Natural Progesterone
4) Avoid carcinogenic chemicals, xenoestrogens, pesticides, etc.
Articles with Related Content
Iodine Supplementation and Breast Cancer Prevention
Mammogram Awareness Month
Rethinking Screening Mammography
Screening Mammograms, a Closer Look at the Data
Update: Karen Kaplan LA Times Feb 2014
Cancer Expert says to Radiologists: Stop Lying About Mammograms
Update Feb 2014 BMJ article says:
"Annual mammography in women aged 40-59 does not reduce mortality from breast cancer beyond that of physical examination or usual care when adjuvant therapy for breast cancer is freely available. Overall, 22% (106/484) of screen detected invasive breast cancers were over-diagnosed, representing one over-diagnosed breast cancer for every 424 women who received mammography screening in the trial."
Twenty five year follow-up for breast cancer incidence and mortality of the Canadian National Breast Screening Study: randomised screening trial BMJ 2014; 348 doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/bmj.g366 (Published 11 February 2014) Cite this as: BMJ 2014;348:g366
Jeffrey Dach MD
7450 Griffin Rd Suite 180/190
Davie, FL 33314
Phone: 954-792-4663
Facebook
Blog
Links and References
1)Rethinking Screening for Breast Cancer Laura Esserman JAMA 2009.pdf
448.5 KB
Rethinking Screening for Breast Cancer and Prostate Cancer
Laura Esserman, MD, MBA; Yiwey Shieh, AB; Ian Thompson, MD JAMA. 2009;302(15):1685-1692.
After 20 years of screening for breast and prostate cancer, several observations can be made. First, the incidence of these cancers increased after the introduction of screening but has never returned to prescreening levels. Second, the increase in the relative fraction of early stage cancers has increased. Third, the incidence of regional cancers has not decreased at a commensurate rate. One possible explanation is that screening may be increasing the burden of low-risk cancers without significantly reducing the burden of more aggressively growing cancers and therefore not resulting in the anticipated reduction in cancer mortality. To reduce morbidity and mortality from prostate cancer and breast cancer, new approaches for screening, early detection, and prevention for both diseases should be considered.
Stop Calling it Cancer
http://consensus.nih.gov/2009/dcisstatement.htm
Conclusions: Clearly, the diagnosis and management of DCIS is highly complex with many unanswered questions, including the fundamental natural history of untreated disease. Because of the noninvasive nature of DCIS, coupled with its favorable prognosis, strong consideration should be given to elimination of the use of the anxiety-producing term “carcinoma” from the description of DCIS. The outcomes in women treated with available therapies are excellent. Thus, the primary question for future research must focus on the accurate identification of patient subsets diagnosed with DCIS, including those persons who may be managed with less therapeutic intervention without sacrificing the excellent outcomes presently achieved. Essential in this quest will be the development and validation of accurate risk-stratification methods based on a comprehensive understanding of the clinical, pathologic, and biologic factors associated with DCIS.
http://www.medpagetoday.com/HematologyOncology/BreastCancer/16538
Analysis Questions Breast and Prostate Cancer Screening
By Peggy Peck, Executive Editor, MedPage Today October 21, 2009
http://movingtotheusa.blogspot.com/2009/10/rethinking-strategies-for-breast-and.html
Thursday, 22 October 2009. Rethinking strategies for breast and prostate cancer screening. Twenty years of screening for breast and prostate cancer—the most diagnosed cancers for women and men—have not brought the anticipated decline in deaths from these diseases, argue experts in an opinion piece published Wednesday in the Journal of the American Medical Association
Gilbert Welch MD
http://www.vaoutcomes.org/welch.php
H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH Professor of Medicine and Community and Family Medicine, Dartmouth Medical School; Co-Director of the White River Junction Outcomes Group
Research Interests: Dr. Welch is a general internist whose research focuses on the problems created by medicine's efforts to detect disease early: physicians test too often, treat too aggressively and tell too many people that they are sick. Most of his work has focused on overdiagnosis in cancer screening: in particular, screening for melanoma, cervical, breast and prostate cancer. His recent book, "Should I be tested for cancer? Maybe not and here's why" (UC Press 2004)
http://www.vaoutcomes.org/papers/NYT_cancer_screening.pdf
How Two Studies on Cancer Screening Led to Two Results - New York Times March 13, 2007
http://8.12.42.31/2008/nov/03/opinion/oe-welch3
The excessive focus on mammography. Looking harder to find more may not be the best practice. By H. Gilbert Welch November 03, 2008
http://www.nytimes.com/2008/10/07/health/views/07essa.html
Campaign Myth: Prevention as Cure-All By H. GILBERT WELCH, M.D October 6, 2008
http://www.bmj.com/cgi/content/full/339/jul09_1/b1425
9 July 2009, BMJ 2009;339:b1425 Editorials. Gilbert Welch MD. Overdiagnosis and mammography screening. The question is no longer whether, but how often, it occurs.
Huffington Post Helen Cordes
http://www.huffingtonpost.com/helen-cordes/
rethink-pink-now-saner-so_b_329496.html
Rethink Pink NOW! Saner Solutions to Breast Cancer, Part 2
Spontaneous Remission of Breast Cancer
http://archinte.ama-assn.org/cgi/content/abstract/168/21/2311?ijKey=aa7696d7321cedbb1eba2e4864792009cd8250c4&keytype2=tf_ipsecsha
The Natural History of Invasive Breast Cancers Detected by Screening Mammography Per-Henrik Zahl, MD, PhD; Jan Mæhlen, MD, PhD; H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH Arch Intern Med. 2008;168(21):2311-2316.
http://www.nytimes.com/2008/11/25/health/25breast.html?pagewanted=1&_r=2
Study Suggests Some Cancers May Go Away By GINA KOLATA November 24, 2008
Others, Miscellaneous
PSA Screening for Cancer, the Failed Medical Experiment by Jeffrey Dach MD
http://www.greenhealthspot.com/2009/10/rethinking-cancer-screening.html
Rethinking Cancer Screening Dr Wang
http://www.dbtechno.com/health/2009/10/21/study-says-screening-for-breast-cancer-is-over-rated/
Study says screening for breast cancer is over rated
http://jeffreydach.com/2009/08/16/the-thyroid-nodule-epidemic-by-jeffrey-dach-md.aspx
The Thyroid Nodule Epidemic by Jeffrey Dach MD
DCIS
http://theoncologist.alphamedpress.org/cgi/content/full/12/11/1276
The Oncologist, Vol. 12, No. 11, 1276-1287, November 2007; Current Treatment and Clinical Trial Developments for Ductal Carcinoma In Situ of the Breast. Judy C. Bougheya, Ricardo J. Gonzalezb, Everett Bonnerc, Henry M. Kuererb
autopsy studies show silent reservoir of breast cancer
http://www.annals.org/cgi/content/full/127/11/1023
Using Autopsy Series To Estimate the Disease "Reservoir" for Ductal Carcinoma in Situ of the Breast: How Much More Breast Cancer Can We Find? H. Gilbert Welch, MD, MPH, and William C. Black, MD ANnals of Internal Med 1 December 1997 | Volume 127 Issue 11 | Pages 1023-1028. The reported incidence of DCIS has increased more than fourfold since 1980 [7]; this type of cancer now accounts for nearly half of mammographically detected cases of cancer [8, 9]. Whereas the two series with the highest prevalence (both of which were performed by the same investigators) were the most assiduous: The investigators examined 95 and 275 specimens per breast after being guided by radiographs of each 5-mm section.
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2002422/?tool=pubmed
Br J Cancer. 1987 December; 56(6): 814–819. PMCID: PMC2002422
Breast cancer and atypia among young and middle-aged women: a study of 110 medicolegal autopsies. M. Nielsen, J. L. Thomsen, S. Primdahl, U. Dyreborg, and J. A. Andersen Department of Pathology, Frederiksberg Hospital, Copenhagen, Denmark. In 110 consecutive, medicolegal autopsies of young and middle-aged women (range 20-54 years) the breasts were examined by an extensive histopathologic method and by correlative specimen radiography. Malignancy was found in 22 women (20%) of which only one was known to have had clinical invasive breast cancer (IBC). At autopsy 2 women had IBC (2%), the remaining in situ carcinoma (in situ BC) of microfocal type (18%), i.e. 15 (14%) intraductal carcinomas (DCIS), 4 (3%) lobular carcinoma in situ (LCIS) and one (1%) both DCIS and LCIS.
Incidence and Mortality Stats
http://www.cancer.org/downloads/STT/F861009_final%209-08-09.pdf
Breast Cancer Facts and Figures 2009,2010 American Cancer Society
http://www.cancer.org/docroot/stt/stt_0.asp
breast cancer facts and figures 2009 ACS. Stage: Figure 5b (page 7) presents incidence trends by race and stage at diagnosis. The incidence of regional-stage disease increased during 1994-2001 and has since decreased on average by 2.8% per year. Incidence rates of distant-stage disease have remained stable.
http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html
It is estimated that 192,370 women will be diagnosed with and 40,170 women will die of cancer of the breast in 2009.
The following information is based on NCI’s SEER Cancer Statistics Review2X Close Breast Section (http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2006/results_merged/sect_04_breast.pdf )
Incidence & Mortality Breast Cancer Mortality Rates Continue to Decline. According to a report issued by the American Cancer Society, breast cancer death rates in the United States continue to decline by more than 2% per year. This and other breast cancer statistics were published in Breast Cancer Facts & Figures 2009-2010.
Breast cancer mortality rates began to decline in the U.S. in 1990, and the most recent statistics suggest that this decline is continuing. Nevertheless, an estimated 40,170 women will die of breast cancer in 2009
http://caonline.amcancersoc.org/cgi/content/full/59/4/225
CA Cancer J Clin 2009; 59:225-249 Cancer Statistics, 2009 Ahmedin Jemal, DVM, PhD1, Rebecca Siegel, MPH2, Elizabeth Ward, PhD3, Yongping Hao, PhD4, Jiaquan Xu, MD5 and Michael J. Thun, MD, MS6
TABLE 8 Trends in the Recorded Number of Deaths from Selected Cancers by Sex, United States, 1990–2006
1990 43,391 deaths from breast cancer
2006 40,821 deaths from breast cancer
Source: US Mortality Data, 1990 to 2006, National Center for Health Statistics, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2009.
http://seer.cancer.gov/statistics/
It is estimated that 192,370 women will be diagnosed with and 40,170 women will die of cancer of the breast in 2009. Table I-1 (http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2006/results_single/sect_01_table.01.pdf).
Naomi Freundlich
http://www.alternet.org/healthwellness/143195/saving_women_from_breast_cancer%3A_are_mammograms_really_the_answer/
Saving Women From Breast Cancer: Are Mammograms Really the Answer? By Naomi Freundlich, Health Beat. Posted October 21, 2009.
"For every 2,000 women [age 50-69] invited for screening throughout 10 years, one will have her life prolonged. In addition, 10 healthy women who would not have been diagnosed if there had not been screening, will be diagnosed as breast cancer patients and will be treated unnecessarily. It is thus not clear whether screening does more good than harm.
H. Gilbert Welch, professor of medicine at Dartmouth Institute for Health Policy and Clinical Research, writing in an editorial in the British Medical Journal looks at the "credits" and "debits" a 50-year-old woman considering yearly mammography should consider (figures are per 1000 women):
•1 in 1,000 women annually screened for 10 years will avoid dying from breast cancer.
•2 to 10 women will be over-diagnosed and treated needlessly
•10 to 15 women will be told they have breast cancer earlier than they would otherwise have been told, but this will not affect their prognosis.
•100 to 500 women will have at least one "false alarm" (about half of these women will undergo a biopsy)
Welch adds, "Mammography is one of medicine's 'close calls'-- a delicate balance between benefits and harms—where different people in the same situation might reasonably make different choices. Mammography undoubtedly helps some women but hurts others. No right answer exists, instead it is a personal choice."
http://www.timesonline.co.uk/tol/comment/letters/article5761650.ece?token=null&offset=0&page=1
February 19, 2009. Breast cancer screening peril. Negative consequences of the breast screening programme. Peter C. Gøtzsche and his colleagues from the independent Nordic Cochrane Centre. They describe a synthesis of published papers that quantify the benefits and harms of screening using absolute rather than relative numbers that make it easier to comprehend. They conclude as follows: if 2,000 women are screened regularly for ten years, one will benefit from the screening, as she will avoid dying from breast cancer. At the same time, ten healthy women will, as a consequence, become “cancer patients” and will be treated unnecessarily.
http://breastcanceradvocate.wordpress.com/
2009/10/01/the-truth-about-breast-cancer-is-not-pretty-and-its-not-pink/
The Truth About Breast Cancer is Not Pretty and it’s not Pink Posted October 1, 2009
http://ww5.komen.org/contentsimpleleft.aspx?id=6442451356&itc=lefthpban:77
Comments on Mammography Leading to Over-Diagnosis and Over-Treatment (Dr. Eric Winer, October 2009)
http://www.cbcrp.org/publications/papers/Mayer/page_08.php
Changes in Breast Cancer Mortality Rates,
A 2002 article in the New York Times,22 in which Dr. Barnett Kramer, director of the Office of Disease Prevention at the National Institutes of Health, “This phenomenon is largely attributable to mammography,” according to the New York Times article: “The number of women with breast cancers with the worst prognosis, those that spread to other organs, had been fairly constant in the years before mammography was introduced, and that trend did not change after the introduction of mammography.”
Clearly, Dr. Kramer was suggesting that early detection had failed to live up to its promise. “If screening worked perfectly,” the article continues, “every cancer found early would correspond to one fewer cancer found later. That, he (Kramer) said, did not happen.
Mammography, instead, has resulted in a huge new population of women with early stage cancer but without a corresponding decline in the numbers of women with advanced cancer.” The modest size of the reductions in later stage cancers and the unchanged status of metastatic disease are troubling. It appears that the early-detection approach to reducing cancer mortality fails to take into account the reality that some tumors are so aggressive that even the earliest detection will fail to eradicate them, while others are so indolent that it seems to make little difference if they are found before they become palpable. The burden of advanced breast cancer shows no real sign of abating, and is likely to continue and even increase as treatments prolong life.
In Figure 7, the SEER data for 25-year breast cancer incidence rates by stage, as well as death rates, are presented in graphic form. The top line, representing localized breast cancer clearly shows the precipitous rise begun in the early 1980s, with the dashed reddish line indicating the trend. The other clearly ascending line, accompanied by a dashed reddish line, is for in situ breast cancer, also associated with increased mammography screening. The dashed purplish trendlines for both the regional breast cancer rates and deaths show only slight decreases. There has been no change in the rate of distant (metastatic) breast cancer diagnosed over twenty-five years.
http://www.nytimes.com/2002/04/09/
science/confronting-cancer-breast-cancer-mammography-finds-more-tumors-then-debate.html
CONFRONTING CANCER; Breast Cancer: Mammography Finds More Tumors. Then the Debate Begins. By Gina Kolata Published: Tuesday, April 9, 2002
http://nosurrenderbreastcancer.blogspot.com/2009/10/acs-throws-women-under-bus.html
Wednesday, October 21, 2009
ACS Throws Women Under the Bus. The American Cancer Society has lobbed a deadly volley over the bow of SS Cancerland...
http://www.ratical.org/radiation/CNR/XHP/MPDaXrayST.html
Making Personal Decisions about X-ray Screening Tests, Such as Mammography and CT of the Lung, Colon, Heart, or the Entire Body. John W. Gofman, M.D., Ph.D., Professor Emeritus of Molecular & Cell Biology, University of California at Berkeley. Egan O'Connor, Executive Director and Editor, CNR. "
Spontaneous Remission Regression of Cancer
http://www.noetic.org/research/sr/main.html
Spontaneous Remission. largest database of medically reported cases of spontaneous remission in the world, with more than 3,500 references from more than 800 journals in 20 different languages.
The Medical Aspects of Carcinoma of the Breast, with a Note on the Spontaneous Disappearance of Secondary Growths OSLER W American Medicine: April 6 1901; 17-19; 63-66 Extracted Summary
The consulting physician sees mammary cancer at two stages of its progress. Dreading the
surgeon, and hoping against hope, a number of women prefer to come to him at the first detection of a tumor. But these form a small fraction of the cases. A large majority are the unhappy victims of the internal metastases after operation. For some years I have been interested in this class of cases, and have collected material bearing upon the question of these late, and more strictly medical, manifestations of the disease.
In this paper, fourteen cases of carcinoma of the breast are reported in which there were
secondary growths and in some cases the secondary growths spontaneously disappeared.
http://www.auntminnie.com/index.asp?sec=ser&sub=def&pag=dis&ItemID=87566
'Spontaneous regression' debate erupts anew at ASCO symposium By Kate Madden Yee AuntMinnie.com staff writer October 12, 2009
Mouse Model of Spontaneous Regression
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC164507/
Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003 May 27; 100(11): 6682–6687. The National Academy of Sciences. Immunology
Spontaneous regression of advanced cancer: Identification of a unique genetically determined, age-dependent trait in mice. Zheng Cui et al.
Jeffrey Dach MD
7450 Griffin Road Suite 190
Davie, Florida 33314
954-792-4663
http://www.drdach.com/
http://www.naturalmedicine101.com/
http://www.truemedmd.com/
http://www.bioidenticalhormones101.com/
Disclaimer click here: http://www.drdach.com/wst_page20.html
The reader is advised to discuss the comments on these pages with
his/her personal physicians and to only act upon the advice of his/her
personal physician. Also note that concerning an answer which appears as
an electronically posted question, I am NOT creating a physician —
patient relationship.
Although identities will remain confidential as much as possible, as I can not control the media, I can not take responsibility for any breaches of confidentiality that may occur.
Copyright (c) 2014 Jeffrey Dach MD All Rights Reserved
This article may be reproduced on the internet without permission,
provided there is a link to this page and proper credit is given.
FAIR USE NOTICE: This site contains copyrighted material the use of which has not always been specifically authorized by the copyright owner. We are making such material available in our efforts to advance understanding of issues of significance. We believe this constitutes a ‘fair use’ of any such copyrighted material as provided for in section 107 of the US Copyright Law. In accordance with Title 17 U.S.C. Section 107, the material on this site is distributed without profit to those who have expressed a prior interest in receiving the included information for research and educational purposes.
Serving Areas of: Hollywood, Aventura, Miami, Fort Lauderdale, Pembroke Pines, Miramar, Davie, Coral Springs, Cooper City, Sunshine Ranches, Hallandale, Surfside, Miami Beach, Sunny Isles, Normandy Isles, Coral Gables, Hialeah, Golden Beach ,Kendall,sunrise, coral springs, parkland,pompano, boca raton, palm beach, weston, dania beach, tamarac, oakland park, boynton beach, delray,lake worth,wellington,plantation